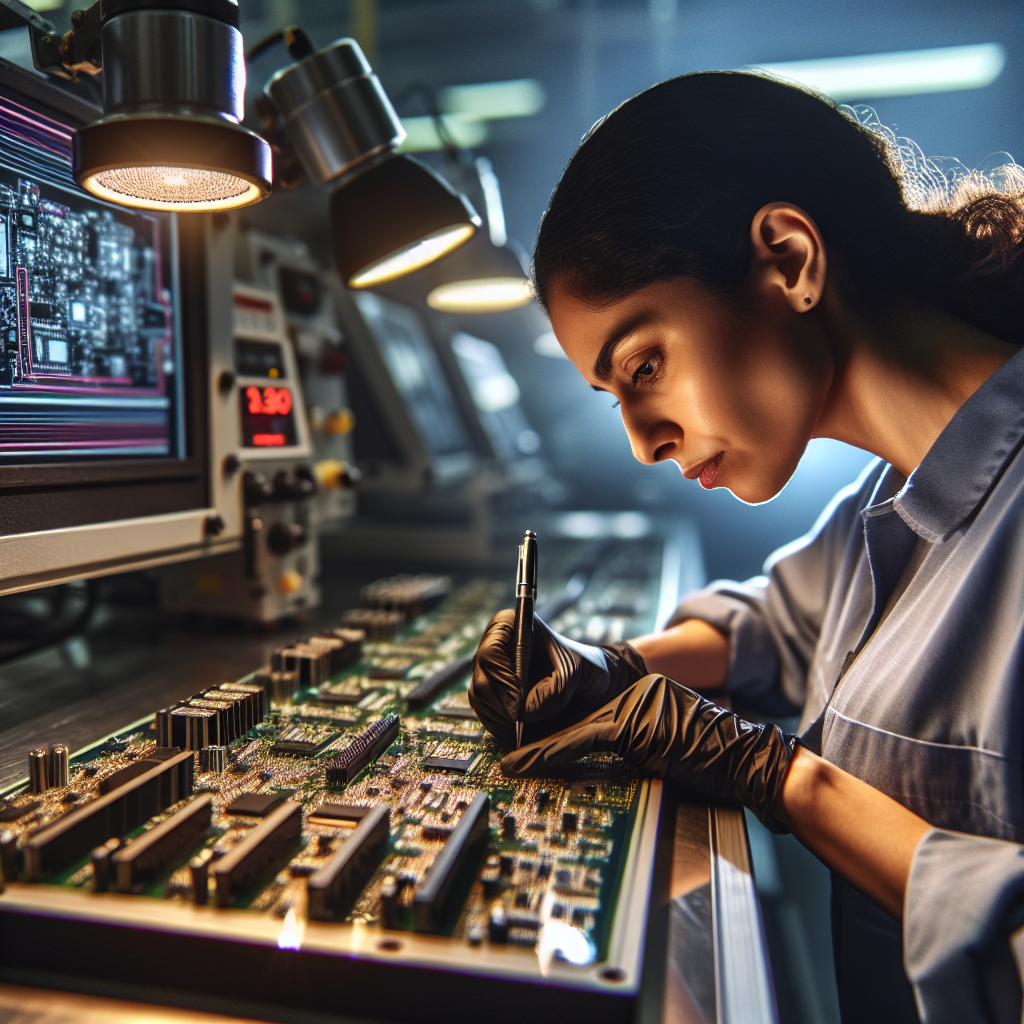
When it comes to industrial automation and medical devices, the quality of your printed circuit board assembly (PCBA) can make all the difference. I recently came across an intriguing article about high-quality PCBA assembly services that feature Surface-Mount Technology (SMT), Dual In-line Package (DIP) assembly, and comprehensive testing capabilities. This suite of services is especially appealing for those of us involved in the industrial automation sector, where performance and reliability are non-negotiable. Let’s embark on a deep dive into what makes these services essential, how they bolster automation projects, and what to consider as you leverage PCBA assembly for your applications.
Table of Contents
- What is PCBA?
- Understanding the PCBA Process
- Importance of PCBA in Industrial Automation
- Services Offered in PCBA Assembly
- Quality Assurance and Testing in PCBA
- Choosing the Right PCBA Provider
- The Future of PCBA Assembly for Automation
- Summary
- FAQs
- Sources
What is PCBA?
PCBA stands for Printed Circuit Board Assembly. It refers to both the method and the finished product created by soldering electronic components onto a pre-designed printed circuit board (PCB). In essence, the PCBA is what brings a PCB to life. Before this process, the board is simply a collection of conductive traces and pads without any active electronics. Through the assembly process, the circuit board is populated with chips, resistors, capacitors, connectors, and other vital components.
Understanding the PCBA Process
The modern PCBA process is a finely tuned combination of precision, automation, and quality control. Here are the key stages you’ll typically encounter:
- Solder Paste Application: Solder paste is first applied to the bare board in areas where parts are to be mounted.
- Pick and Place: Automated machines place tiny, surface-mount components onto the board at high speeds.
- Reflow Soldering: The board travels through a reflow oven, melting solder paste and permanently bonding the components.
- DIP (Through-Hole Insertion): For larger parts, leads are inserted into pre-drilled holes and soldered, often by hand or wave soldering machines.
- Inspection and Testing: Automated optical inspection (AOI), X-ray inspection, and electrical testing ensure assembly integrity.
This combination of automated and manual steps supports the diversity of components found in advanced applications like automation equipment and medical devices.
Importance of PCBA in Industrial Automation
Within the industrial automation sphere, the reliability and performance of machinery and automated systems heavily depend on the underlying electronics. The PCBA, as the core of most control and monitoring devices, plays a central role in ensuring that processes run uninterrupted and safely. Assemblies must withstand high vibration, electrical noise, and changing environmental factors.
High-quality PCBA assemblies reduce the risk of failures, prevent unexpected downtime, and can even enhance the throughput and precision of entire production systems. According to Automation.com, investing in reputable PCBA partners and top-tier assembly standards can dramatically improve the efficiency and resilience of manufacturing lines. For original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), this translates into greater customer trust, less maintenance overhead, and the freedom to innovate without worrying about catastrophic failure at the electronics level.
For mission-critical sectors like medical technology, PCBA not only influences performance but can be a direct determinant of patient safety and compliance with international standards.
Services Offered in PCBA Assembly
Modern PCBA service providers offer an expansive suite of assembly and testing capabilities, far beyond simple soldering. The most important offerings you can leverage include:
- Surface Mount Technology (SMT): SMT enables the placement of miniature components directly onto the surface of circuit boards. Advantages of SMT include support for more compact devices, dual-sided assembly, and increased circuit complexity in a smaller footprint. SMT is the dominant assembly technique in today’s high-speed, high-density electronics.
- DIP (Through-Hole) Assembly: While increasingly replaced by SMT, through-hole assembly remains essential for large or specialized components that need extra mechanical support or thermal resilience. DIP-mounted parts are commonly found in high-power industrial devices, heavy connectors, and some sensors.
- Comprehensive Testing: Testing is vital for catching errors and validating both the assembly quality and the electronic performance of the finished boards. Services commonly include AOI, in-circuit testing (ICT), functional testing, and even environmental stress testing—ensuring that boards perform under real-world conditions typical in factories or hospitals.
- Prototyping and Low-Volume Production: Many providers support rapid prototyping and short runs, allowing you to iterate designs quickly and economically before ramping into mass production.
- Turnkey Manufacturing: Some advanced PCBA partners can even source components, manage inventories, handle logistics, and provide value-added engineering solutions—freeing designers and engineers to focus on innovation.
These capabilities are particularly critical for innovation-focused industries where both flexibility (rapid prototyping) and reliability (rigorous testing) are non-negotiable requirements.
Quality Assurance and Testing in PCBA
Quality assurance (QA) is foundational to any reputable PCBA service. Given the complexity and density of today’s circuit boards, even minor assembly errors can have major downstream effects. As a result, stringent quality protocols are essential both during and after assembly.
Key aspects of PCBA quality assurance include:
- Incoming Material Inspection: Suppliers verify that all PCBs and components meet specifications before assembly begins.
- Process Control: Automated equipment tracks placement accuracy, solder volume, and oven profiles in real time.
- Automated Optical Inspection (AOI): High-resolution cameras check for misaligned, missing, or poorly soldered parts—often immediately after placement or reflow.
- X-ray Inspection: X-ray machines are used to verify the solder joints for parts located underneath chips, such as BGAs (ball grid arrays).
- Electrical Testing: In-circuit and functional tests verify that the board meets requisite performance criteria.
- Environmental Testing: For mission-critical industries, boards are placed in high-heat, high-humidity, or vibration environments to simulate years of real-world operation.
This multifaceted testing regime is especially important in industrial automation and medical sectors, where defective boards could halt lines or even endanger patients. Choosing a PCBA supplier with rigid QA standards—and the certifications to prove it—is paramount.
Choosing the Right PCBA Provider
With so many PCBA services on the market, how do you select the right one? The stakes, particularly in automation and healthcare, are simply too high for guesswork. Before engaging a provider, consider these criteria:
- Experience with Your Sector: Look for assemblers with a demonstrable history in industrial automation or medical device electronics. Trend reports and reviews from resources like TechCrunch often spotlight innovators and reliable manufacturers to watch.
- Certifications: For automation, ISO 9001 is a bare minimum; for medical devices, ISO 13485 is essential. IPC-A-610 standards also provide assurance of workmanship quality.
- Customer Reviews and References: Ask for testimonials or references from customers with similar applications. Independent insights can reveal how a provider handles challenges or special requests.
- Advanced Capabilities: Ensure your provider offers AOI, X-ray inspection, and robust testing. Extra capabilities like conformal coating, failure analysis, and complete supply chain management are also valuable for complex projects.
- Scalability: Does the provider have the ability to support your growth—from small prototype batches to large-scale volume runs?
Establishing a partnership with a PCBA supplier—rather than treating it as a purely transactional relationship—can also yield long-term dividends. Many top providers offer ongoing engineering support, design for manufacturability (DFM) guidance, and proactive obsolescence management.
The Future of PCBA Assembly for Automation
Looking toward the future, PCBA assembly for automation and healthcare devices is poised for dramatic technological advances. Some trends and innovations to watch include:
- Ultra-high-density Interconnects: Boards are becoming ever more compact, packing more computing power and sensory inputs into smaller, ruggedized spaces. This requires precision robotic placement and advanced inspection systems.
- Flexible and Wearable PCBs: Automation and healthcare devices are increasingly wearable or integrated into irregular surfaces—demanding flexible, even stretchable, substrates for PCBA.
- AI-Driven Quality Control: Advanced software now helps inspect boards for faults faster than any human, driving down error rates and supporting traceability through machine learning.
- Green Manufacturing: Environmental sustainability is becoming a selection factor; top providers are adopting lead-free solder, solvent-free cleaning, and circular economy practices.
- Integrated IoT and Wireless: Modern PCBA must support not just basic computation but robust, secure wireless communication, allowing automation devices to be remotely monitored or controlled.
This evolution means that selecting a forward-looking PCBA assembly partner isn’t just about today’s needs, but ensuring your solutions are future-proofed for tomorrow’s challenges.
Summary
High-quality PCBA assembly services aren’t just a technical detail—they’re central to the success and longevity of industrial automation and medical designs. By understanding what PCBA is, why it matters, which services are critical, and how to find the right partner, you can give your projects a foundation built to last. As devices become smarter and more connected, investing in world-class PCBA assembly is an investment in your ability to innovate and meet your industry’s most demanding standards. Remember, the board inside your device is as important as the software or mechanics that surround it.
FAQs
- What is the difference between SMT and DIP? SMT (Surface Mount Technology) places small, flat components directly onto PCB surfaces, enabling compact, high-density assemblies. DIP (Dual In-line Package) involves inserting larger, pin-leaded parts through holes in the board, often for added mechanical stability.
- How can I ensure the quality of my PCBA? Engage providers with ISO certifications and proven, documentable quality control processes including full inspection, testing, and traceability. Request test reports and, where possible, visit facilities to see their operations in person.
- Why is PCBA important for medical devices? Medical electronics demand absolute reliability. A single failed board could mean downtime for critical care equipment, with significant patient risks. Regulatory requirements also mandate strict traceability and quality documentation at every PCBA stage.
- What is involved in functional testing? Functional testing simulates real-world operating conditions, ensuring the board not only works electrically but interacts correctly with its intended peripherals and software. It’s a final, crucial check before delivery to the end user.
- How does PCBA affect time to market? Modern PCBA assembly services, particularly those with rapid prototyping and automated testing, accelerate your design iteration cycles—enabling faster launches and more agile responses to customer feedback or requirements changes.